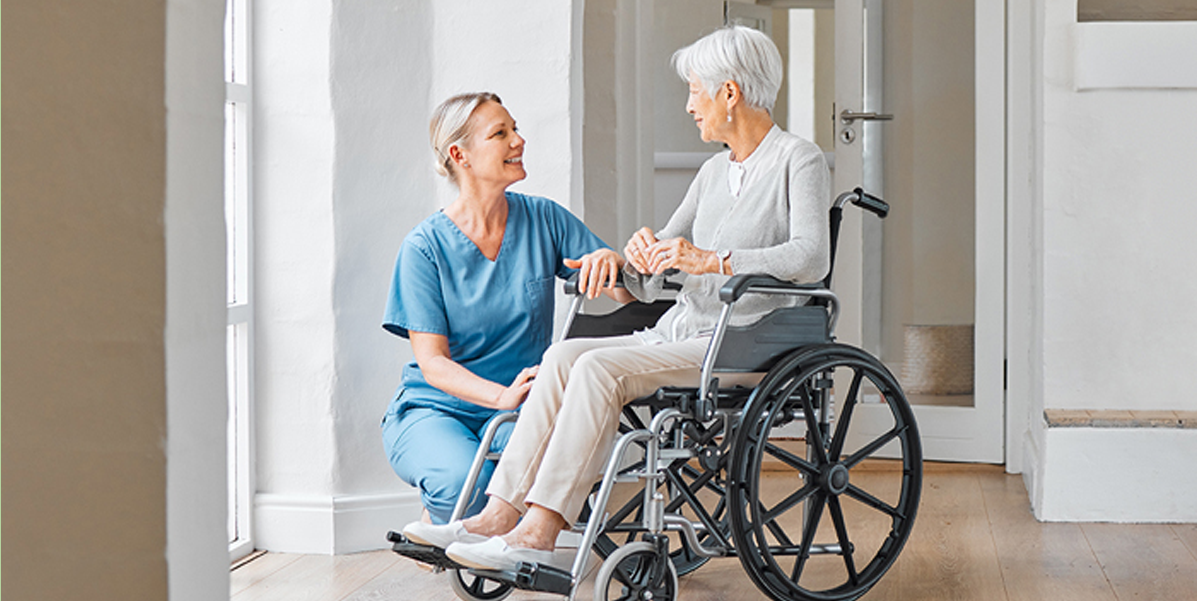
Respite care plays a crucial role in supporting carers and individuals with disability, chronic illness, or age-related needs. In Queensland, legal frameworks around guardianship and consent are essential to ensure that care is provided safely, ethically, and in line with the rights of care recipients. This article explores guardianship, decision-making, consent requirements, legal responsibilities, and best practices for respite care providers and families in Queensland. What is Guardianship in Queensland? Guardianship is a legal arrangement where a person, known as a guardian, is authorised to make decisions on behalf of someone who lacks the capacity to make those decisions themselves. In Queensland, guardianship is regulated under the Guardianship and Administration Act 2000 (Qld). Key points about guardianship include: For respite care, guardians often provide consent for care arrangements, access to services, and participation in activities. Understanding Consent in Respite Care Consent is a fundamental principle in health, disability, and aged care services. It ensures that care recipients or their legally authorised representatives agree to the services provided. In respite care, consent typically covers: Consent must be informed, voluntary, and documented. Providers should ensure that the care recipient or guardian understands the nature of the service, associated risks, and alternatives. Assessing Capacity for Decision-Making Before seeking consent, it is crucial to assess the participant’s capacity to make decisions. In Queensland, a person may be considered to lack capacity if they are unable to: When a person has capacity, they should provide consent themselves. Guardians are only involved when the individual cannot make informed decisions independently. Legal Frameworks Governing Guardianship and Consent Several Queensland laws and national frameworks guide guardianship and consent in respite care: 1. Guardianship and Administration Act 2000 (Qld) 2. Health and Disability Legislation 3. NDIS Practice Standards 4. Privacy Legislation Consent for Short-Term and Long-Term Respite Respite care can be short-term (a few hours to a few weeks) or long-term (extended stays for ongoing relief). Consent procedures differ slightly based on the duration and intensity of care: Providers must ensure consent is recorded and stored appropriately in care records for accountability and compliance. Role of Guardians in Behaviour Support and Restrictive Practices Some respite participants may require behaviour support due to cognitive impairments or challenging behaviours. In these cases: Failing to obtain proper consent for restrictive practices can result in serious legal consequences for providers. Responsibilities of Respite Care Providers Respite care providers have a legal and ethical duty to ensure that guardianship and consent requirements are followed: Dispute Resolution and Guardianship Conflicts Occasionally, conflicts may arise between guardians, family members, or care recipients regarding respite care arrangements. Providers should: Best Practices for Guardianship and Consent in Respite To ensure compliance and protect care recipients’ rights, providers should: Conclusion Understanding guardianship and consent is critical for safe, ethical, and legally compliant respite care in Queensland. Providers must ensure that care recipients’ rights, autonomy, and wellbeing are prioritised while adhering to state and federal laws. By following proper consent procedures, recognising guardianship authority, maintaining accurate documentation, and regularly reviewing care plans, providers can deliver high-quality respite services that protect both participants and carers. Guardianship and consent are not just legal requirements—they are essential tools for empowering care recipients, supporting families, and fostering trust in respite care services across Queensland.
The Crucial Role of Caregivers in Supporting Individuals with Disability The Crucial Role of Caregivers in Supporting Individuals with Disability Today, the care and support provided to disabled individuals play a vital role in ensuring their overall well-being, independence, and inclusion. Caregivers, whether they are family members, friends, or professionals, act as pillars of strength, compassion, and guidance for disabled individuals. Let’s explores the significant role of caregivers in supporting disabled members, highlighting their contributions in fostering physical, emotional, and social well-being. Physical Support One of the fundamental responsibilities of caregivers is to provide physical support to disabled individuals. This includes assisting with daily activities such as personal hygiene, mobility, and medication management. Caregivers help disabled individuals navigate their environment, ensuring they have access to necessary resources and aids. They may also accompany them to medical appointments, therapy sessions, and other healthcare-related activities. Through their assistance, caregivers contribute to improving the physical health and overall quality of life of disabled individuals. Emotional Support Living with a disability can often lead to emotional challenges and psychological distress. Caregivers play a critical role in providing emotional support to disabled members, fostering a sense of security, empathy, and understanding. They offer a listening ear, a comforting presence, and a source of encouragement. By being attentive to the emotional needs of disabled individuals, caregivers help alleviate feelings of isolation, anxiety, and depression. Through their unwavering support, caregivers enable disabled individuals to develop resilience, confidence, and a positive outlook on life. Social Support Social interaction and inclusion are essential for the well-being of disabled individuals. Caregivers act as advocates and facilitators, promoting social integration and participation. They may assist in organizing social events, recreational activities, and outings, ensuring that disabled members have opportunities to engage with their community. Caregivers also help bridge the communication gap between disabled individuals and the wider society, promoting understanding and acceptance. By fostering social connections, caregivers contribute to enhancing the overall quality of life and sense of belonging for disabled individuals. Advocacy and Empowerment Caregivers serve as advocates for disabled individuals, promoting their rights, needs, and interests. They navigate complex systems, such as healthcare, education, and employment, ensuring that disabled members have access to appropriate services and opportunities. Caregivers empower disabled individuals by fostering self-advocacy skills, encouraging independence, and facilitating decision-making processes. Through their advocacy efforts, caregivers strive to break down barriers, challenge stereotypes, and create inclusive environments that empower disabled individuals to live fulfilling lives. Education and Skill Development Caregivers play a pivotal role in facilitating the education and skill development of disabled members. They work closely with educational institutions, teachers, and therapists to ensure that appropriate accommodations and support are provided. Caregivers also engage in teaching practical skills, such as self-care, communication techniques, and adaptive strategies, enabling disabled individuals to navigate their daily lives with greater independence. By fostering learning opportunities, caregivers equip disabled individuals with the tools and knowledge necessary to overcome challenges and achieve personal growth. The role of caregivers in supporting disabled individuals is multifaceted and indispensable. Q1 Care in Queensland has been helping families by providing them services of Personal Carers in Chapel Hill, Disability Support in Richlands along with Domestic Help in Oxley. They provide physical, emotional, and social support, act as advocates, empower disabled individuals, and facilitate their education and skill development. Caregivers embody compassion, resilience, and dedication, and their contributions are instrumental in enhancing the overall well-being and quality of life for disabled members. Society must recognize, appreciate, and support caregivers to ensure they can continue to fulfill their crucial role in supporting disabled individuals effectively. Together, caregivers and disabled individuals can forge a path towards inclusivity, equality, and a more compassionate society. Recent Posts All Post General The Crucial Role of Caregivers in Supporting Individuals with Disability August 9, 2023 Fun Activities for Elderly People with Disabilities August 9, 2023 How to Handle Epilepsy: a neurological disorder! August 9, 2023
Fun Activities for Elderly People with Disabilities Fun Activities for Elderly People with Disabilities Engaging in enjoyable activities can greatly enhance the well-being and quality of life for seniors with disabilities. Here are six fun activities that can be adapted to accommodate various disabilities: Arts and Crafts: Encourage seniors to express their creativity through arts and crafts. Provide materials for painting, drawing, sculpting, or even simple activities like colouring. Adaptations such as larger paintbrushes, easy-to-grip pencils, or tactile materials can be used to accommodate different disabilities. Music Therapy: Music can be a powerful tool for relaxation and enjoyment. Organize music therapy sessions where seniors can listen to their favorite songs, sing along, or play musical instruments. Consider using adaptive instruments or assistive devices if necessary. Gardening: Gardening offers a therapeutic and rewarding experience for seniors. Create accessible raised garden beds or container gardens that can be easily reached from a seated position. Seniors can plant flowers, herbs, or vegetables and take pleasure in watching their plants grow. Board Games and Puzzles: Engage seniors in entertaining and mentally stimulating activities such as board games and puzzles. Choose games with larger print or tactile features for those with visual impairments. Adaptations like card holders or magnifying glasses can also be helpful. Chair Exercises and Yoga: Physical activity is crucial for maintaining mobility and overall health. Modify exercise routines to accommodate seniors with disabilities, focusing on seated exercises or chair yoga. These activities can improve strength, flexibility, and balance. Storytelling and Reminiscence: Encourage seniors to share their life stories and memories through storytelling sessions. This can foster social interaction and create a sense of connection. Provide prompts, such as old photographs or meaningful objects, to stimulate reminiscence. We must always remember, it’s important to consider individual needs and abilities when planning activities for seniors with disabilities. Consulting with healthcare professionals or activity coordinators who specialize in working with seniors can also provide valuable insights and guidance. If you are looking for NDIS registered caregivers for family members, friends, or acquaintances, having mobility issues or any other form of disability, you can reach out to Q1 care today. They are providing support to people with disabilities in areas like Inala, Springfield, Richlands, Durack, Augustine Heights, Acacia Ridge. Q1 care provide caregivers for nursing, daily household task, travel assistance, high intense activities, along with development of life skills to people living across Australia. With their sincere care givers operating in different parts of Queensland, they have established a goodwill in the community. Recent Posts All Post General Fun Activities for Elderly People with Disabilities August 9, 2023 How to Handle Epilepsy: a neurological disorder! August 9, 2023
How to Handle Epilepsy: a neurological disorder! How to Handle Epilepsy: a neurological disorder! Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent and unpredictable seizures. Seizures are episodes of abnormal and excessive electrical activity in the brain. These electrical disturbances can cause a wide range of symptoms, which vary depending on the area of the brain affected by the abnormal activity. Epilepsy is a chronic condition, meaning it persists over time. It can develop at any age and can be caused by various factors, including genetics, brain injuries, infections, developmental disorders, and more. In some cases, the exact cause of epilepsy may not be identified. Seizures associated with epilepsy can take many forms, including: Generalized Seizures: These involve widespread electrical disturbances in the brain and can affect consciousness. Subtypes of generalized seizures include: Tonic-Clonic Seizures (Grand Mal): Characterized by convulsions, loss of consciousness, stiffening of muscles (tonic phase), followed by rhythmic jerking (clonic phase). Absence Seizures: Brief lapses of consciousness where the person may appear to be staring into space and may not remember the episode afterward. Atonic Seizures: Also known as “drop attacks,” these involve sudden loss of muscle tone, causing the person to collapse. Partial (Focal) Seizures: These seizures originate in a specific area of the brain and can be classified into: Simple Partial Seizures: The person remains conscious but experiences unusual sensations, emotions, or movements. Complex Partial Seizures: These affect consciousness and can cause repetitive behaviors or movements, confusion, and memory loss. Epilepsy diagnosis is typically based on a careful medical history, observation of seizure activity, and diagnostic tests such as electroencephalogram (EEG) to record brain activity during a seizure. Brain imaging scans like MRI or CT scans may also be used to identify any structural abnormalities. Treatment for epilepsy aims to control or reduce the frequency and severity of seizures. This often involves medications called antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), as well as lifestyle modifications, such as managing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding seizure triggers. In cases where seizures are not well-controlled by medication, other treatment options like surgery, ketogenic diet, vagus nerve stimulation, or responsive neurostimulation might be considered. Here are some common treatment options: Medications: Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are usually the first-line treatment for epilepsy. There are many different AEDs available, and the choice of medication depends on the type of seizures and the patient’s medical history. A doctor will work to find the most effective medication with the fewest side effects. Lifestyle Modifications: Certain lifestyle changes can help manage epilepsy. These may include getting enough sleep, avoiding triggers like alcohol or stress, and maintaining a consistent routine. Ketogenic Diet: This high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet can sometimes be effective for managing epilepsy, especially in children who do not respond well to medications. It should only be done under the supervision of a medical professional. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): This involves implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, which can help reduce the frequency and severity of seizures. Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS): A device is implanted in the brain to monitor brain activity and deliver targeted stimulation when abnormal activity is detected. Surgery: For some patients whose seizures are not well-controlled with medications, surgery might be considered. This could involve removing the part of the brain responsible for triggering seizures. Support and Counseling: Epilepsy can have psychological and emotional impacts. Counseling and support groups can provide valuable assistance in coping with the condition. Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that might provoke seizures can help manage the condition. Triggers can vary widely between individuals. Regular Medical Check-ups: Regular visits to a neurologist or epileptologist are essential to monitor the patient’s condition, adjust medications if necessary, and discuss any concerns. It’s important to remember that epilepsy treatment should be tailored to the individual patient’s needs, and treatment plans may need to be adjusted over time. If you or someone you know has epilepsy, it’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop an appropriate treatment plan. Recent Posts All Post General The Crucial Role of Caregivers in Supporting Individuals with Disability August 9, 2023 Fun Activities for Elderly People with Disabilities August 9, 2023 How to Handle Epilepsy: a neurological disorder! August 9, 2023